The Excel ADDRESS Function returns a cell address for specified row and column coordinates. Optional arguments allow you to specify the style of address (A1 or R1C1), the sheet name it refers to and whether the reference is absolute or relative.
Excel ADDRESS Function Syntax
| Syntax: | =ADDRESS(row_num, column_num, [abs_num], [a1], [sheet_text]) |
Note: Arguments in square brackets are optional.
At its most basic the ADDRESS Function requires two arguments, the row and column numbers:
=ADDRESS(1,1)
=$A$1
| row_num | Numeric value that specifies the cell reference's row number |
| column_num | Numeric value that specifies the cell reference's column number |
| [abs_num] | Numeric value that specifies whether the reference returned is absolute or relative. An absolute reference is returned if this argument is omitted. See table below. |
| [abs_num] | Returns a reference that is: | |
| 1 or omitted | Absolute | |
| 2 | Absolute row; relative column | |
| 3 | Relative row; absolute column | |
| 4 | Relative |
| [a1] | Specifies the reference style; A1 or R1C1: |
| TRUE or 1 | returns the A1 reference style where rows are numbered, and columns labeled alphabetically. | |
| FALSE or 0 | returns R1C1 reference style where rows and columns are numbered.. |
| [sheet_text] | A text value that allows you to specify the sheet the reference is on. |
| e.g. =ADDRESS(1,1,1,1,"Sheet4") returns Sheet4!$A$1. If this argument is omitted the address returned refers to a cell on the current sheet. |
Download the Workbook
Enter your email address below to download the sample workbook.
Excel ADDRESS Function Examples
The table below contains examples with varying abs_num and style [A1] arguments (notice the sheet_text argument is omitted in these examples):
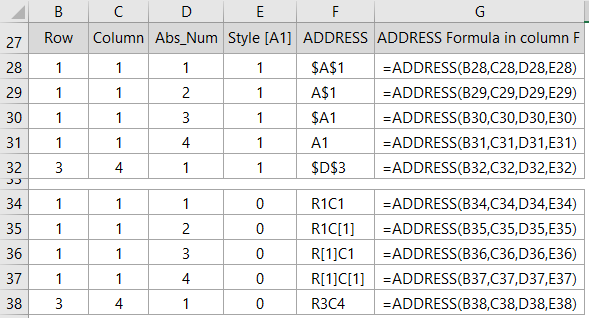
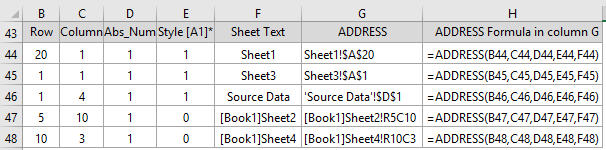
The references above all assume they refer to the current sheet, but if you want to return an address that refers to a different sheet or a different workbook, then you can use the sheet_text argument like so:
Return the Cell ADDRESS of a Named Range
It can be handy to keep a record of the cell references your named ranges refer to, particularly if they’re dynamic. For example, cells B53:C58 in the image below are named Rng.
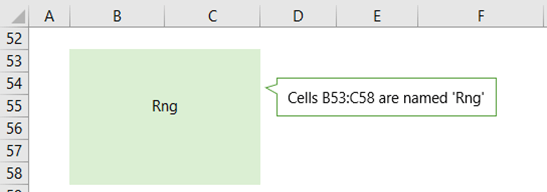
I can use the ADDRESS function to document the first cell in the range
=ADDRESS(ROW(Rng),COLUMN(Rng),1,1)
=ADDRESS(53,2,1,1)
=$B$53
The last cell in the range:
=ADDRESS(ROW(Rng)+ROWS(Rng)-1,COLUMN(Rng)+COLUMNS(Rng)-1,1,1)
=ADDRESS(53+6-1,2+2-1,1,1)
=$C$58
Or the complete range:
=ADDRESS(ROW(Rng),COLUMN(Rng),1,1)&":"&ADDRESS(ROW(Rng)+ROWS(Rng)-1,COLUMN(Rng)+COLUMNS(Rng)-1,1,1)
=ADDRESS(53,2,1,1)&":"&ADDRESS(53+6-1,2+2-1,1,1)
=$B$53:$C$58
The row and column number vales are calculated using the ROW, ROWS, COLUMN and COLUMNS functions.
- ROW returns the row number
- ROWS returns number of rows in a range
- COLUMN returns the column number
- COLUMNS returns the number of columns in a range
More on the ROW, ROWS, COLUMN and COLUMNS functions.
Tip: If you just want to find the address of a cell, then the CELL function is simpler:
=CELL("address",Rng)
=$B$53
Caution: Notice that CELL only returns the address of the first cell in Rng, so it's great for single cells or for returning the first cell in a range.
Convert an ADDRESS to a Cell Reference
If you want to use the ADDRESS function to return a reference to a cell, while nested inside another function, then you need to wrap it in INDIRECT.
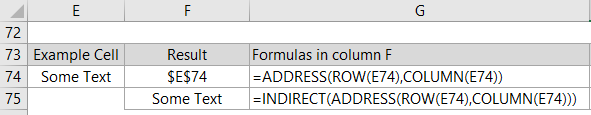
For example; cell E74 in the image below contains a text string. The ADDRESS Function using ROW and COLUMN simply returns the cell reference, but if you actually want to evaluate the cell reference, in other words return the value in cell E74, then you need to wrap the ADDRESS formula in INDIRECT.
More on the INDIRECT function here.
Excel ADDRESS Function Errors
#VALUE! In the ADDRESS function this generally signals the wrong type of argument. Typically, one or more of the first 3 arguments will be wrong. E.g. specifying an abs_num argument value > 4.
#NAME? This error can be triggered in the ADDRESS function when you incorrectly enter the style or abs_num argument, or specify the row or column number with anything other than a number.
More Examples of the ADDRESS Function
- Highlight cells referenced in Excel formulas
- Dynamic hyperlinks that update based on a selection
- Dynamic hyperlink lookup
Please Share
If you liked this please click the buttons below to share.







Mynda, you are great!
🙂 thanks, Sandeep! Glad I can help.
Though you have provided examples of how to use the ADDRESS function, I’ve never been able to figure out a reason to use it.
The use case that I generally have is a change log for a financial model, in which I’m trying to record which specific cells in a model were changed. For that purpose, I want to show a pointer on each line of the log to identify which the changed cells. For this purpose, I use the following one line VBA function.
Function celladdress(arg As Object) As String
‘===========================================================
‘ returns the address of the cell specified
‘ ‘===========================================================
celladdress = “=” & arg.Worksheet.Name & “!” & arg.Address
End Function
Hi Jason,
You’ll have to stick with your VBA solution for the change log because formulas are constantly updating, they can tell if something is in a cell or not, but if you change that value they can’t tell you something changed.
There are 3 tutorials at the bottom that link to examples of the ADDRESS Function in use, plus under the heading “Return the Cell ADDRESS of a Named Range” I explain how to use it to document cell ranges for named ranges, and finding the first and last cells in a range.
Hope that helps.
Mynda
Awesome tutorial, Mynda, you have the gift to explain the things so clearly that everything complex is an easy task. Keep up the great work!
Thank you, Juan 🙂