You may already know you can find the 3rd highest value using the LARGE function, but what if you want to average the top 3 values in a long list like the one below?
Enter your email address below to download the sample workbook.
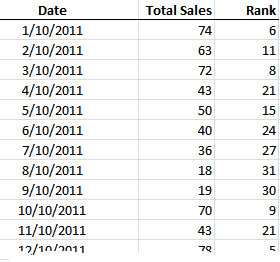
=AVERAGE(LARGE(sales,{1,2,3}))
Our data range is the ‘Total Sales’ column and it’s named ‘sales’.
But what if your data range sometimes has less than 3 values?
The above formula would return an error, so we need to get a bit clever…
Now, like loads of things in Excel there are many ways to skin a cat so I’m just going to show you one way.
It uses 5 different functions! But don’t be put off as you’ll learn some great tricks in this tutorial that you can apply to other problems.
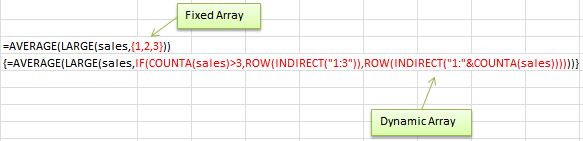
Here’s the formula:
{=AVERAGE(LARGE(sales,IF(COUNTA(sales)>3,ROW(INDIRECT("1:3")), ROW(INDIRECT("1:"&COUNTA(sales))))))}
Note: remember to enter an array formula you need to press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER together to insert the curly brackets at the beginning and end of the above formula. You don’t type them in yourself.
“YIKES”, I hear you say. Deep breath…keep reading.
Let’s break it down and translate it into English:
{=AVERAGE(the LARGEst values in the sales range, IF(the number of values in the ‘sales’ range is >3 then average the first 3, if not count the number of values and average those).}
Effectively we’re replacing the fixed array in the first formula with functions that will calculate this array on the fly, thus allowing the number of items in the array to be less than 3.
Note: you could use the AVERAGEIF function instead of the IF and AVERAGE that I have used, but if you only have 2003 you don’t have the luxury of AVERAGEIF.
So let’s look at the functions we’ve used:
AVERAGE Function
Easy peasy lemon squeezy (as my 5 year old would say). But if you don’t know AVERAGE it’s simply =AVERAGE(then enter your data range, or the numbers you want to average separated by commas)
=AVERAGE(A1:A50) or =AVERAGE(50,65,25,30,81)
LARGE Function
Also easy peasy lemon squeezy. Click here for more on the LARGE function.
COUNTA Function
Counts the cells in a range that are not empty. Click here for more on the COUNTA function.
ROW Function
Returns the ROW number of a reference. =ROW(B12) will return 12.
INDIRECT Function
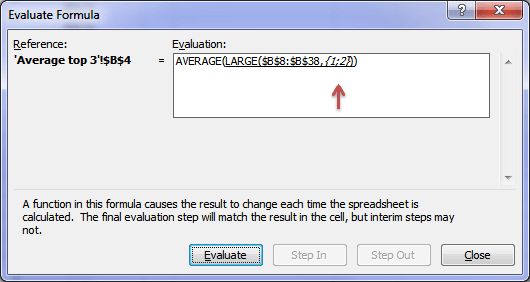
The INDIRECT function allows you to create a reference to a range of cells by referencing other cells, or in this example an array. Huh? Let’s look at an example from our formula above:
INDIRECT("1:"&COUNTA(sales))
Let’s assume there are 2 values in the ‘sales’ data range. The COUNTA will return a 2.
And you use the ampersand symbol ‘&’ to join the components of your reference together, just as I’ve done above.
The result of this section of the formula is 1:2, as you can see in the Evaluate Formula box below.
Ok, so now we can follow what’s actually going on in this formula I want to share one other much simpler option that only applies in Excel 2007+.
It uses the IFERROR function that is not available in Excel 2003:
=IFERROR(AVERAGE(LARGE(sales,{1,2,3})),AVERAGE(sales))
The first part of the formula is the same as our simple fixed array mentioned at the beginning, and the second part allows for an error if there are less than 3 values, by simply averaging what’s left.
For more tips like this sign up to our weekly Excel Tips & Tricks newsletter below.


A2 Cell value = A (name of person)
from B2 to F2 I have different values of marks in 5 subjects.
I created =topavg(B2:F2,$H$1) where ‘topag’ is recursive LAMBDA
=LAMBDA(range,n,
IF(n=1,LARGE(range,n),
topavg(AVERAGE(LARGE(range,n)),n-1)))
But its not working. I want to get average of top ‘n’ numbers from given range, which I would have normally doing as =AVERAGE(LARGE(B2:F2,1),LARGE(B2:F2,2)…….)
Requesting your help in this LAMBDA. Not sure where I am going wrong.
Hi Rajan,
I’m not sure you need a recursive LAMBDA. Please post your question and sample Excel file with several examples which illustrate why you need a recursive LAMBDA on our forum where we can help you further: https://www.myonlinetraininghub.com/excel-forum
Mynda